Prerequisites
Virtualization platform
Introduction
Late in July, Ioannis Koniaris of BruteForce Lab (Greece)
released HoneyDrive 3, the Royal Jelly edition. When Team Cymru’s Steve
Santorelli sent out news of same to the Dragon News Bytes list the little light
bulb went off in my head. As I prepared to write our ninety-sixth toolsmith for
October’s edition I realized I had not once covered any honeypot technology as
the primary subject matter for the monthly column. Time to rectify that
shortcoming, and thanks to Ioannis (and Steve for the ping on DNB radar screen)
we have the perfect muse in HoneyDrive 3.
From HoneyDrive 3’s own description, it’s a
honeypot Linux distro released as a virtual appliance (OVA) running Xubuntu
Desktop 12.04.4 LTS edition which includes over 10 pre-installed and
pre-configured honeypot software packages. These includes the Kippo SSH
honeypot, Dionaea and Amun malware honeypots, the Honeyd low-interaction
honeypot, Glastopf web honeypot and Wordpot, Conpot SCADA/ICS honeypot, as well
as Thug and PhoneyC honeyclients and more. It also includes many useful
pre-configured scripts and utilities to analyze, visualize and process the data
it captures, such as Kippo-Graph, Honeyd-Viz, DionaeaFR, an ELK stack and much
more. Finally, nearly 90 well-known malware analysis, forensics and network
monitoring related tools are included with HoneyDrive 3 .
Ioannis let me know he started HoneyDrive mostly out of
frustration arising from the difficulty of installing and configuring some of
the well-known honeypot systems. At first, he created scripts of his own to
automate their installation and deployment but then decided to put them all in
a nice package for two reasons:
1. For
newcomers to be able to quickly deploy and try out various honeypot systems,
2. To
connect the honeypot software with all the existing projects built on top of
them.
As an example Ioannis developed Kippo-Graph, Honeyd-Viz
and various other tools while HoneyDrive makes the integration between the
backend (honeypots) and frontend (tools) seamless. Ioannis has strong evidence
that HoneyDrive and some of the specific tools he’s created are very popular
based on the interactions he’s had online and in-person with various
researchers. HoneyDrive is used in many universities, technical research
centers, government CERTs, and security companies. Ioannis believes honeypots are
more relevant than ever given the current state of global Internet attacks and he
hopes HoneyDrive facilitates their deployment. His roadmap includes creating
visualization tools for honeypot systems that currently don't have any
visualization features, and attempt to develop a way to automatically setup
HoneyDrive sensors in a distributed fashion.
This is a great effort, and it really does not only
simplify setup and getting underway, but the visual feedback is rich. It’s like
having a full honeypot monitoring console and very easy to imagine HoneyDrive
views on big monitors in security operations centers (SOC). Ready to give it a
try?
HoneyDrive Prep
Download the HoneyDrive OVA
via SourceForge.
This is a fully configured 4GB open virtual appliance that you can import into
your preferred virtualization platform. I did so on VMWare Workstation 10, which
complained a bit initially but gave me the option to bypass its whining and
proceed unfettered. There’s a good convert-to-VMWare doc if you
need it but I conducted a direct import successfully. Royal Jelly has run like
a champ since. If you’re exposing the virtual machine in order to catch some
dirty little flies in your honey traps keep in mind that your virtual network
settings matter here. Best to bridge the VM directly to the network on which
you’re exposing your enticing offerings, NAT won’t work so well, obviously.
Apply all the precautions associated with hosting virtual machines that are
likely to be hammered. Depending on where you deploy HoneyDrive and the
specific honeypots you plan to utilize, recognize that it will be hammered, particularly if Internet facing. Worn out, rode
hard and put away wet, flogged…hammered. Feel me? The beauty is that HoneyDrive
does such a fabulous job allowing for performance monitoring, you’ll be able to
keep an eye on it. With virtualization you can always flush it and restart from
your snapshot, just remember to ship off your logs or databases so you don’t
lose valuable data you may have been collecting. Let’s play.
I Am Honeydripper, Hear Me Buzz
There is SO much fun to be
had here, where to begin? Rhetorical…we begin with carefully reading the
comprehensive README.txt file conveniently found on the HoneyDrive desktop.
This README describes all available honeypots and their configurations. You’ll
also find reference to the front-end visualization offerings such as Ioannis’ Kippo-Graph.
Perfect place to get started, Kippo is a favorite.
Kippo
Kippo, like all its
counterparts found on HoneyDrive, is available as a standalone offering, but is
ready in an instant on HoneyDrive. From a Terminator console, cd /honeydrive/kippo followed by ./start.sh. You should receive Starting kippo in the background...Loading dblog
engine: mysql. You’re good to go. If you need to stop Kippo it’s as easy
as…wait for it,./stop.sh. From a
remote system attempt an SSH connection to your HoneyDrive IP address and you
should meet with success. I quickly fired up my Kali VM and pounded the SSH
“service” the same way any ol’ script kiddie would: with a loud bruteforcer. My
favorite it is Patator using
the SSH module and the little John dictionary file from fuzzdb as seen in
Figure 1.
 |
| Figure 1: Bruteforcing Kippo’s SSH service with Patator |
As you can see my very first
hit was successful using that particular dictionary. Any knucklehead with
123456 in their password lists would think they’d hit pay dirt and immediately
proceed to interact. Here’s where Kippo-Graph really shines. Kippo-Graph
includes visual representations of all Kippo activity including Top 10s for
passwords, usernames, combos used, and SSH clients, as well as success ratios,
successes per day/week, connections per IP, successful logins from same IP, and
probes per day/week. Way too many pretty graphs to print them all here, but Kippo-Graph
even includes a graph gallery as seen in Figure 2.
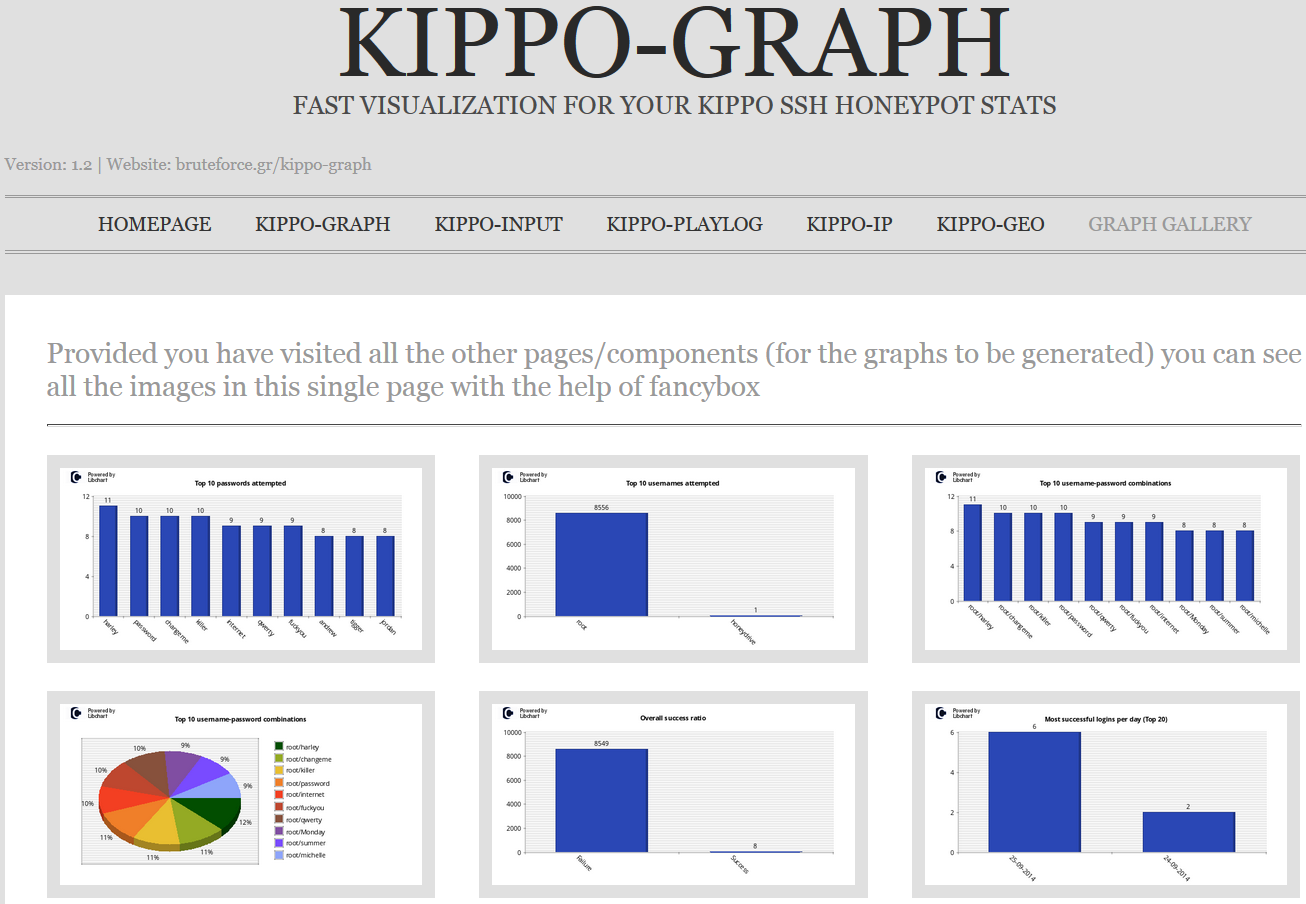 |
| Figure 2: Kippo-Graph’s Graph Gallery shines |
But wait, there’s more. I mentioned
that a bruteforce scanner who believes they are successful will definitely
attempt to login and interact with what they believe is a victim system. Can we
track that behavior as well? Yah, you betcha. Check out Kippo-Input, you’ll see
all commands passed by attackers caught in the honeypot. Kippo-Playlog will
actually playback the attacker’s efforts as video and offering DIG and location
details on the related attacker IP. Figure 3 represents Kippo-Input results.
 |
| Figure 3: Kippo-Input provides the attacker’s commands |
Many of these graphs and
visualizations also offer CSV output; if you wish to review data in Excel or R
it’s extremely useful. HoneyDrive’s Kippo implementation also allows you to
store and review results via the ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) stack,
using Kippo2ElasticSearch, that we first introduced in our toolsmith C3CM
discussions.
Of course, Kippo is not the
only honeypot offering on HoneyDrive 3, let’s explore further.
Dionaea
Per the Honeynet Project site, “Dionaea is a low-interaction honeypot that captures attack
payloads and malware. Dionaea is meant to be a nepenthes successor, embedding
python as scripting language, using libemu to detect shellcodes, supporting
ipv6 and tls.”
HoneyDrive
includes the DionaeaFR script which provides a web UI for all the mayhem
Dionaea will collect.
To
start Dionaea, first cd
/honeydrive/dionaea-vagrant then run ./runDionaea.sh.
Follow this with the following to start DionaeaFR:
cd /honeydrive/DionaeaFR/
python manage.collectstatic
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
Point your browser to http://[your
HoneyDrive server]:8000 and you’ll be presented a lovely UI Dionaea.
Even just an NMAP scan will
collect results in DionaeaFR but you can also follow Dionaea with
Metasploit to emulate malware behavior. Figure 4 is a snapshot of the DionaeaFR
dashboard.
 |
| Figure 4: DionaeaFR dashboard |
You
can see connection indicators from my NMAP scan as well as SMB and SIP exploits
attempts as described in Emil’s Edgis Security blog post.
Wordpot
Wordpot is a WordPress honeypot. No one ever attacks WordPress, right? Want to see how badly WordPress is attacked en masse when exposed to the Internet? Do this:
sudo service apache2 stop (WordPot and
Apache will fight for port 80, suggest moving Apache to a different port anyway)
cd /honeydrive/wordpot
sudo python wordpot.py
You’ll
find the logs in /honeydrive/Wordpot/logs. My logs, as represented along with
my fake WordPress site in Figure 5, are the result of a Burp Suite scan I ran
against it. If you expose WordPot to the evil intarwebs, your logs will look
ridiculously polluted by comparison.
[Insert wordpot.png]
Figure 5: WordPot site and
WordPot logs
A
number of HoneyDrive offerings write to SQLite databases. Lucky for you,
HoneyDrive includes phpLiteAdmin, a web-based SQLite database admin tool
(like phpMyAdmin). Note that is configured to accept traffic only from
localhost by default.
In Conclusion
This is such a great distribution, I’m thrilled Ioannis’
HoneyDrive is getting the use and attention it deserves. If you haven’t
experimented or deployed honeypots before you quite literally have no excuse at
this point. As always, practice safe
honeypotting, no need to actually
suffer a compromise. Honeypots need to be closely monitored, but that’s exactly
what makes HoneyDrive so compelling, great visualization, great logging, and
great database management. HoneyDrive is certainly a front runner for toolsmith
tool of the year, but that, as always, is up to you, my good reader. Download
HoneyDrive ASAP and send me feedback.
Ping me via email if you have questions (russ at
holisticinfosec dot org).
Cheers…until next month.
Acknowledgements
Ioannis Koniaris, project
lead and developer



